Formatting of raw data should be well-documented and reproducible
- Raw data formatting
- The original data files should be saved separately
- Scripts should be developed for raw data formatting to ensure transparent documentation. Manual formatting cannot be documented and may not be reproducible.
- Maintenance of data directory
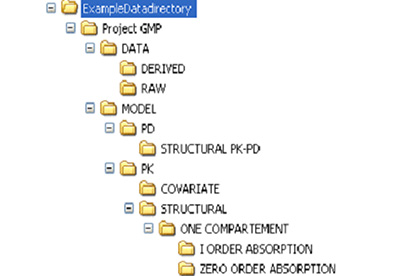
- An example of how a data directory for a project could be maintained is given below:
- Each project could be saved as a separate folder in the personal directory.
- Under each project, there can be two folders, one for data and one for model.
- -----DATA
- -----MODEL
- The DATA folder may contain two folders, one for raw data and one for derived data.
- -----RAW
- -----DERIVED
- The MODEL folder may contain sub folders for PK and/or PD details.
- -----PK
- -----PD
- The PK and/or PD folder could contain the models attempted, which may be stored as subfolders.
- -----STRUCTURAL MODEL
- -----ONE COMPARTMENT
- -----First order absorption
- -----Zero order absorption
- -----TWO COMPARTMENT
- -----ONE COMPARTMENT
- -----COVARIATE MODEL
- -----CL VS AGE
- -----CL vs CLcr and so on...
- -----STRUCTURAL MODEL
- An example of how a data directory for a project could be maintained is given below:
- An example of data directory.
Rational Modeling Process
- Project plan
- Preliminary data analysis
- Determination of initial model
- Covariate model building
- Evaluation of final parameter estimates and model selection
- Model validation/qualification
Report
A population analysis report usually contains the following sections as recommended in the FDA guidance.
- Executive summary
- This is the first section any population analysis report should contain. The summary should be written in an easily understandable language, with no technical terms used. It should provide the gist of the whole analysis in a clear concise manner, easily comprehensible to non-pharmacometricians too.
- Introduction
- Objective, hypotheses and assumptions
- Assay
- Data
- Data analysis methods
- Results
- Discussion
- Application of results
- Appendix
- Electronic format file